Common Loon

Common Loon Information
Length: 28 - 36"
Habitat: Nests on freshwater lakes and rivers. Prefers lakes with islands. Winters mainly on coastal bays and inlets.
Diet: Medium-sized fish; also crustaceans, amphibians, and mollusks; occasionally aquatic plants.
Interesting Facts about the Common Loon
- The Common Loon rarely comes onto land except during mating and the nesting period. Its legs are placed far back on its body, making this bird a powerful swimmer but very awkward on land.
Due its heavy body, the loon is unable to fly directly from land. Instead, it flaps its wings and runs along the surface of the water until it gains enough speed to take off. - Unlike most other birds, loons have solid bones - which increases their weight and plays a part in their excellent diving ability. They have been known to dive up to 200 feet below the surface.
- The Common Loon is well known for its hauntingly beautiful voice. There are four main calls: a wail that is similar to the howl of a coyote, an undulating yodel, a soft hooting call, and a tremulous alarm call (sometimes referred to as "loon laughter").
- In the early fall, Common Loons begin migrating to their winter grounds. They fly during the daytime - either singly or in groups. They spend the winter along the Atlantic, Pacific, and Gulf coasts, and can be found as far south as Mexico.
Common Loon with Chicks

By Michael Heisel on Flickr, CC
Common Loon
Identification Tips
- Large bill is straight, tapers to a point, and is held horizontally
- Feet set far back on body, and trail behind body in flight
- Upperwings wholly dark in flight
- Black bill
- Black neck with white markings
- White chest and belly
- Black back with white checkering and spotting
- Pale gray bill
- Gray-brown cap, forehead, nape, hindneck and back
- White face, eye ring, chin, throat, foreneck and belly
- Jagged border between white foreneck and dark hindneck
- Like basic-plumaged adult but often with paler bill and white scalloping on back
(Credit: U. S. Geological Survey)
Breeding Bird Survey Map,
2011-2015
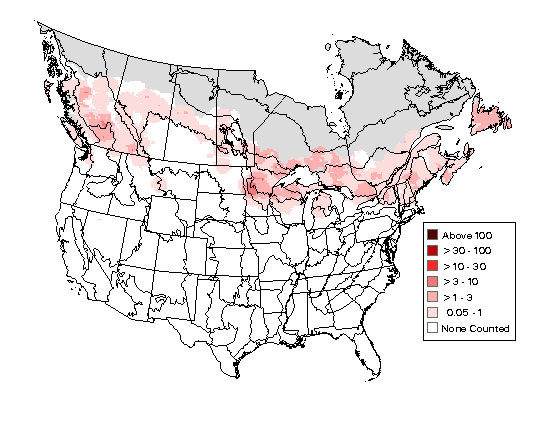
(Image credit: USGS)
Range in New England
The Common Loon breeds in the northern states of New England as well as parts of Massachusetts. This bird is seen in the rest of the region during migration.
In New England, Common Loons migrate in the fall from their freshwater breeding grounds to their wintering areas along the coastline.
Loons that have migrated from eastern Canada will also be found along the New England seaboard. Some loons do remain on their inland breeding grounds during the winter.
Winter Map from eBird
Sightings of the Common Loon
Nov-Mar
over last 10 years![]()
Christmas Bird Count Map
Historical CBC Map from USGS